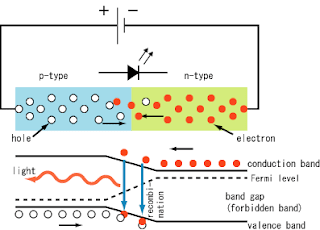
LED physics: as shown in Fig. 1, current flows from the p-side (anode) to the n-side (cathode) when the diode is forward biased. When an electron meets a hole (electron-hole combination), it falls into a lower energy level, and releases energy in the form of a photon.
(Image is from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode)
The wavelength of the light emitted, and therefore its color, depends on the band gap energy of the materials forming the p-n junction.
Photodiodes
Photodiodes are one type of photo detectors (other types includes thermal detectors, photoresistors, photomultipliers, etc.).
Same as LED, a photodiode is a semiconductor p–n junction device. But opposite to LED, in a photodiode light is absorbed in a depletion region and generates a photocurrent. There are two operation modes for a photodiode:
Photovoltaic mode: operated in zero bias. The illuminated photodiode generates a voltage which can be measured. This is photovoltaic effect, which is the basis for solar cells—in fact, a solar cell is just an array of large area photodiodes.
Photoconductive mode: operated in reverse bias (opposite to LED). The resulting photocurrent can be measured. Detectors operated in this mode have high linearity and dynamic range.
| Material | Spectrum range |
|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | 400-1000 nm |
| Germanium (Ge) | 900-1600 nm |
| Indium gallium arsenide phosphide (InGaAsP) | 1000-1350 nm |
| Indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) | 900-1700 nm |
References:
[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode
[2] http://www.rp-photonics.com/photodiodes.html

